How Can We Help?
Search for answers or browse our knowledge base.
Manually Download Files by Select
Purpose
After files have been scanned by the system, they can also be downloaded in their native format. They can either be downloaded individually or in bulk from a local source or a configured target service.
The downloads can reach up to 100MB per download request. If it exceeds this limit, then performing a manual data export is a better option. The system will also download the most up to date version of the file, but if a copy action was previously configured, then an older version can be downloaded from the target service.
When the system contains two or more versions of the same file from different sources, the local host will automatically delete one of the files unless specified otherwise. Downloading and installing 7zip to extract the downloaded files is an effective way to ensure that even files with the same name are still included.
Each time a file is downloaded, the system records the action in an audit log. This allows administrators the ability to query the audit log and display when the files were downloaded and by who.
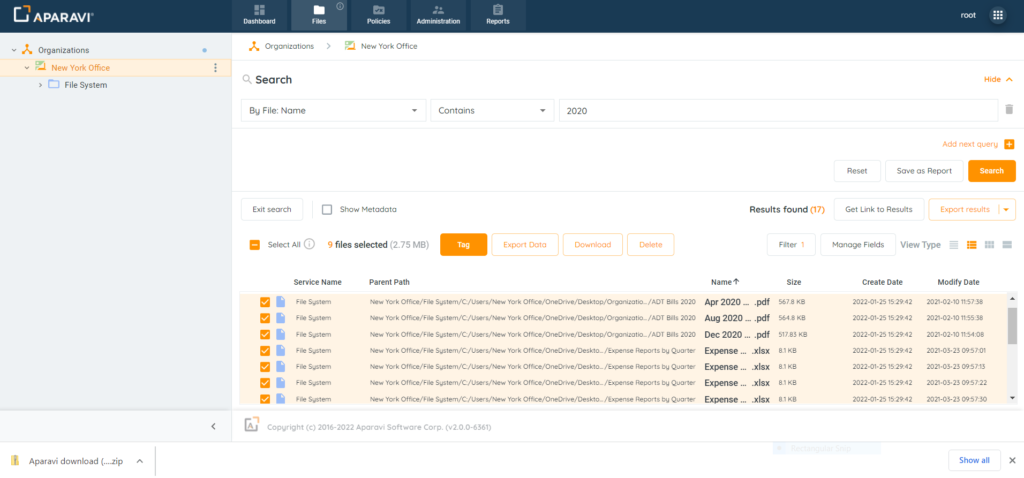
Downloading Files
File Search
1. Click on the Files Tab, located in the top navigation menu.
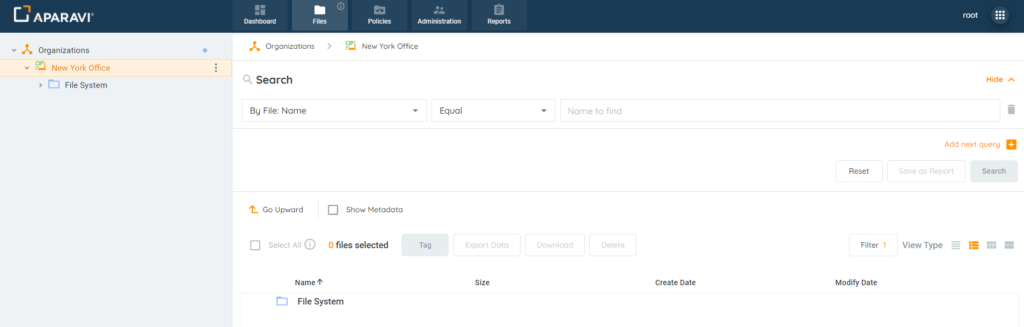
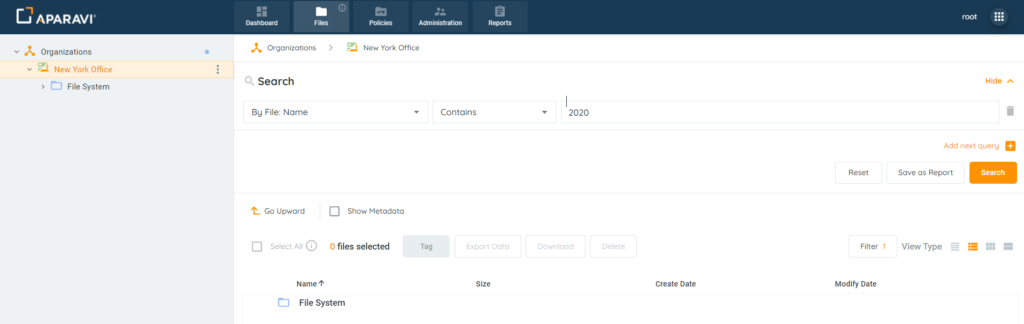
2. Perform any file search using the three query parameters and click the Search button.
3. Select the checkboxes located to the left of the file’s name for download.
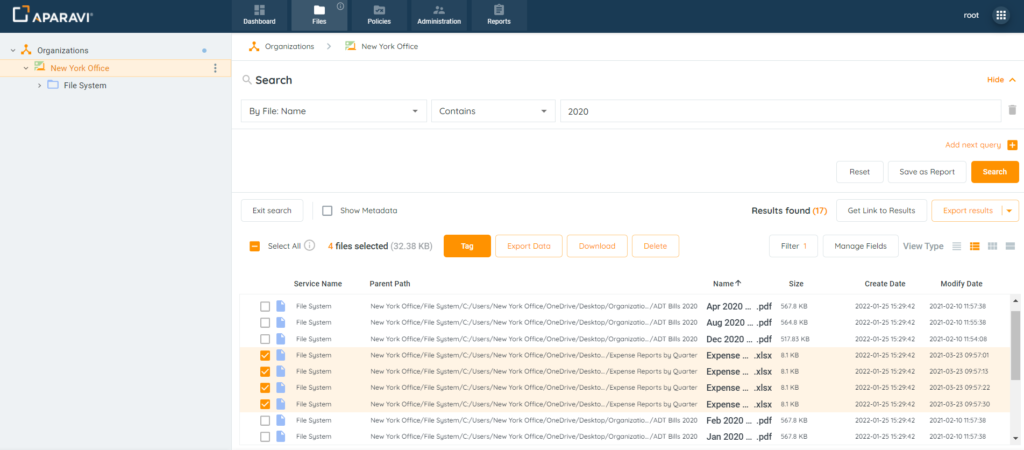
4. Click on the Download button, located at the top of the file results.
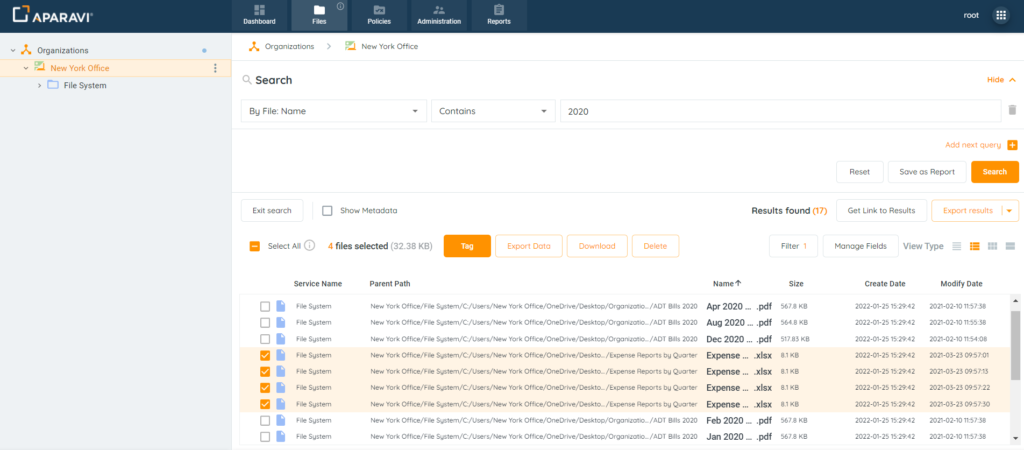
5. The selected files will then automatically be downloaded as a zipped folder to the local host machine. This folder can typically be found in the downloads folder unless specified otherwise.
From this point the files can be extracted from the zipped folder and viewed in their native format.
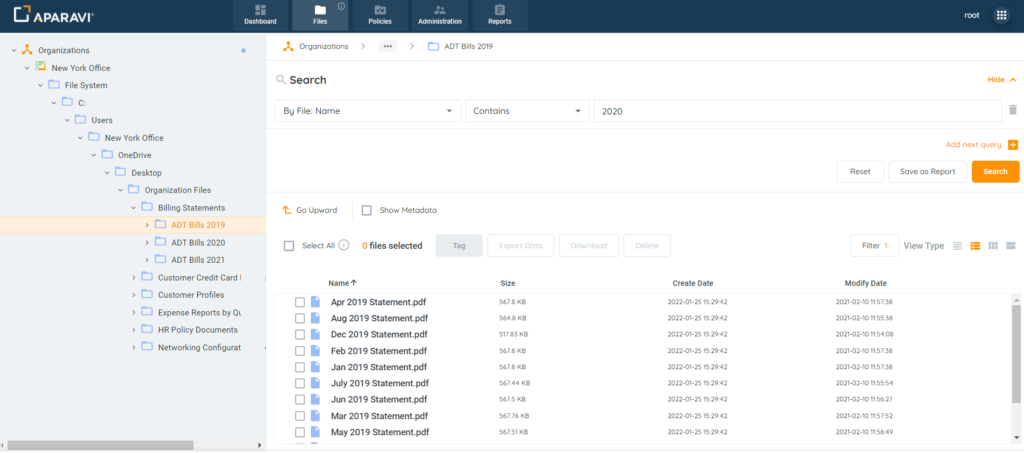
Navigation Tree
1. Located on the left-hand side of the screen, expand the nodes and folders by clicking on the arrows located to the left of their names. Once the folder is reached that contains the files, click on it.
2. Select the checkboxes located to the left of the file’s name for download.
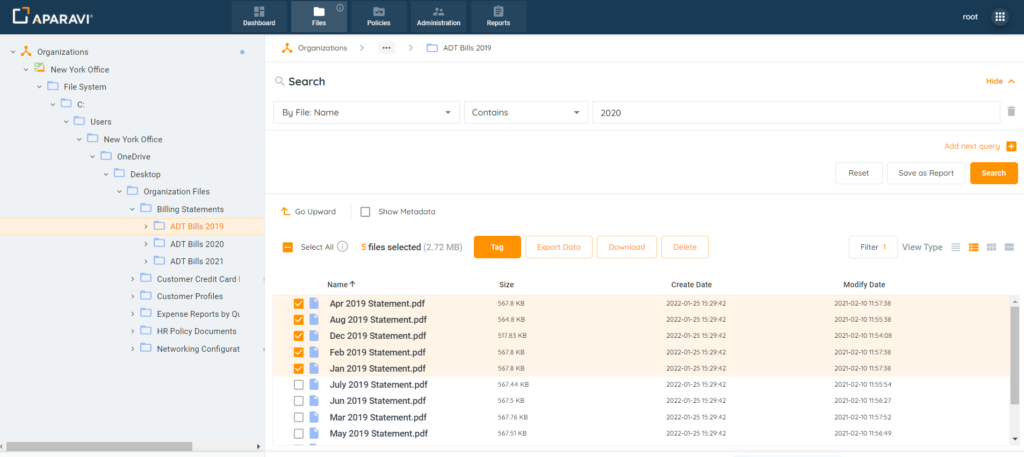
Please Note: various files contained in separate folders cannot be downloaded together using this method. Leaving a folder after selecting files will result in all files being deselected.
3. Click on the Download button, located at the top of the file results.

4. The selected files will then automatically be downloaded as a zipped folder to the local host machine. This folder can typically be found in the downloads folder unless specified otherwise.
From this point the files can be extracted from the zipped folder and viewed in their native format.

Extracting Files From Zipped Folder
When the system contains two or more versions of the same file, from different sources, the local host will automatically delete one of the files unless specified otherwise. If only one file is desired in the download, use the devices OS to extract the files as normal.
If both copies of the files need to be retained, regardless of having the same name, downloading and installing 7zip should be used. Once the program is installed, follow the steps below:
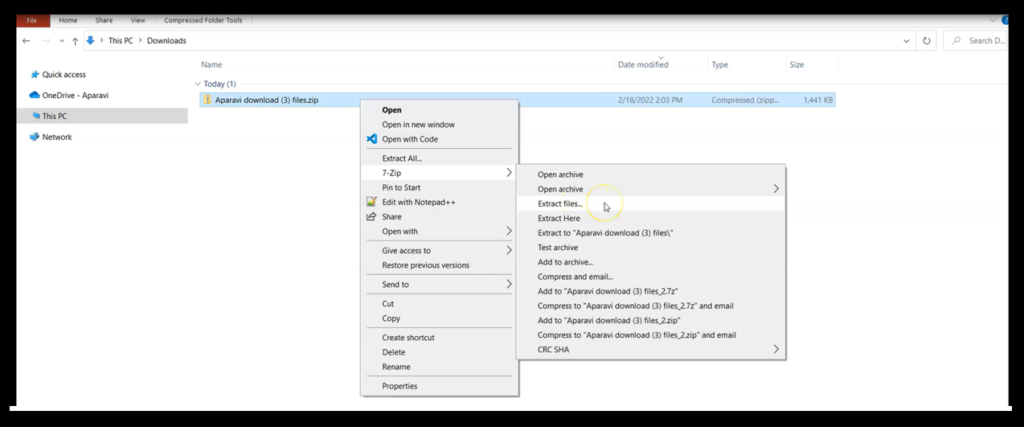
1. Right click on top of the zipped folder and select Extract Files from the 7-Zip sub-menu.

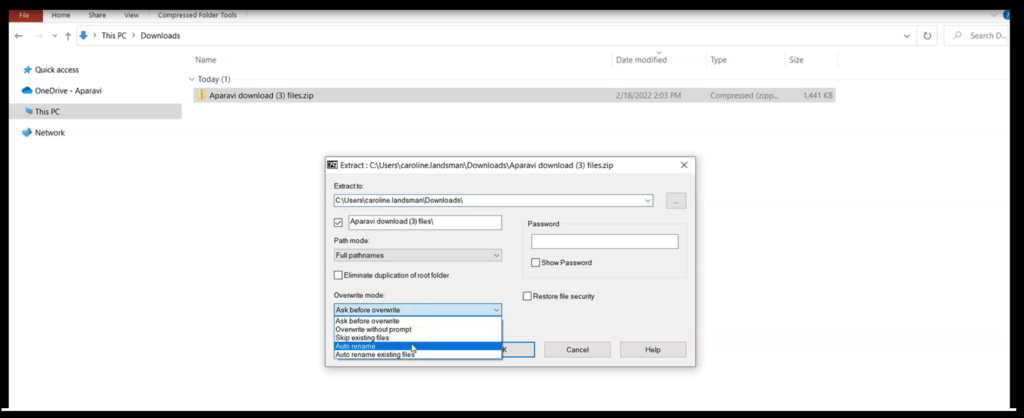
2. Click on the Override mode field and select Auto rename from the drop-down menu. Once completed, click the Ok button to save the changes.

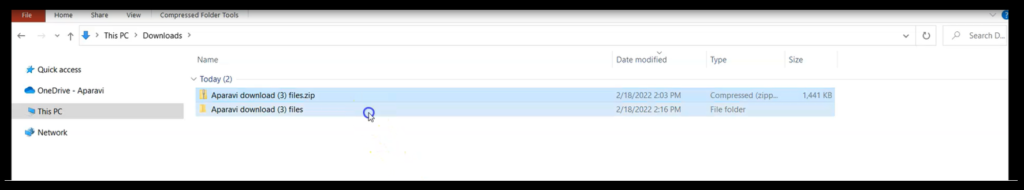
3. The zipped folder will begin to extract the files to an unzipped folder. Click on the unzipped folder to view the downloaded files.

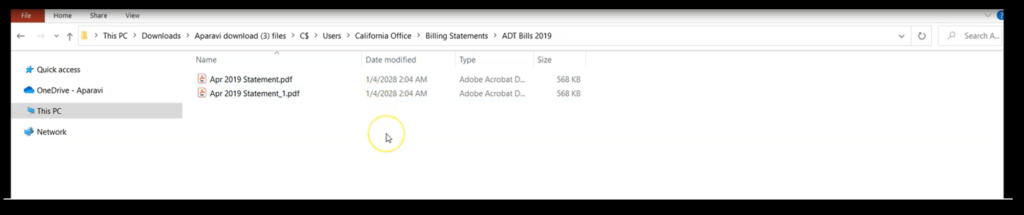
Regardless of the file’s configured source or content, if the files contain the same name, the folder will save both versions of the files. In order to meet the criteria of the OS, the duplicate files will contain variations of the same file name.
Example:
- DownloadedFile.docx
- DownloadedFile_1.docx
- DownloadedFile_2.docx

Handling of Symlinks
Note: There is something important to be aware of in how we treat Symlink downloads.
What is a Symlink?
Symlink is a file whose purpose is to point to a file or directory (called the “target”).
How do we treat such files in Aparavi?
A symlink file, located at the source, may contain absolute or relative paths. However, when scanning a symlink, the link itself is not collected, and such files are not indexed. Additionally, if a user attempts to download a symlink, a 0-length file with no links inside is generated. These security measures apply to both Windows and Linux systems.